Embark on a captivating journey through Unit 1 Geography Challenge Answer Key, where the intricacies of geography unravel before your eyes. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental concepts, regions, physical and human landscapes, and the transformative power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS).
Prepare to expand your geographic horizons and deepen your understanding of our planet.
From grasping the intricacies of latitude and longitude to exploring the diverse regions of the world, this guide serves as an invaluable resource for students and geography enthusiasts alike. Discover the forces that shape our physical environment and the human imprint upon it.
Uncover the complexities of population distribution, urbanization, and globalization. Through engaging examples, interactive maps, and thought-provoking discussions, this guide empowers you to navigate the multifaceted world of geography with confidence.
Geography Concepts and Terms: Unit 1 Geography Challenge Answer Key

Geography is the study of the Earth’s surface and its inhabitants. It encompasses a wide range of topics, including physical geography, human geography, and environmental geography. In this unit, we will explore some of the key concepts and terms used in geography.
Latitude and Longitude
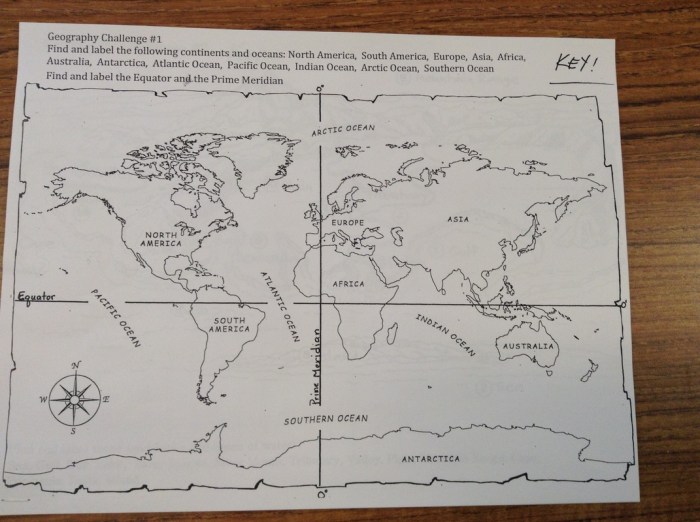
Latitude and longitude are two imaginary lines that are used to locate points on the Earth’s surface. Latitude is the distance north or south of the equator, and longitude is the distance east or west of the prime meridian. Latitude and longitude are expressed in degrees, minutes, and seconds.
Map Projections
A map projection is a way of representing the Earth’s surface on a flat surface. There are many different types of map projections, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some of the most common map projections include the Mercator projection, the Robinson projection, and the Winkel tripel projection.
Scale and Distance
Scale is the ratio of the distance on a map to the distance on the Earth’s surface. Distance is the actual distance between two points on the Earth’s surface. Scale and distance are important concepts in geography because they allow us to measure and compare the size and location of different features.
Regions of the World
The world can be divided into a number of different regions, each with its own unique physical and human characteristics. Some of the major regions of the world include:
North America
- Physical characteristics: North America is a continent that is located in the northern hemisphere. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the east, the Pacific Ocean to the west, and the Arctic Ocean to the north.
- Human characteristics: North America is home to a diverse population of people from all over the world. The region is known for its high standard of living and its advanced economy.
South America, Unit 1 geography challenge answer key
- Physical characteristics: South America is a continent that is located in the southern hemisphere. It is bordered by the Pacific Ocean to the west, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Caribbean Sea to the north.
- Human characteristics: South America is home to a diverse population of people from all over the world. The region is known for its rich culture and its natural beauty.
Europe
- Physical characteristics: Europe is a continent that is located in the northern hemisphere. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Mediterranean Sea to the south.
- Human characteristics: Europe is home to a diverse population of people from all over the world. The region is known for its rich history and its cultural diversity.
Physical Geography
Physical geography is the study of the Earth’s physical features, such as its landforms, water bodies, and climate. Some of the major topics in physical geography include:
Landforms
Landforms are the physical features of the Earth’s surface. They can be classified into two main types: erosional landforms and depositional landforms. Erosional landforms are created by the erosion of the Earth’s surface by water, wind, and ice. Depositional landforms are created by the deposition of sediment by water, wind, and ice.
Water Bodies
Water bodies are the large bodies of water that cover the Earth’s surface. They include oceans, seas, lakes, and rivers. Water bodies are important for a variety of reasons, including providing water for drinking, irrigation, and transportation.
Climate
Climate is the long-term average of weather conditions in a particular area. Climate is determined by a number of factors, including latitude, altitude, and distance from the ocean. Climate can have a significant impact on the plants and animals that live in an area.
Human Geography
Human geography is the study of the relationship between humans and their environment. Some of the major topics in human geography include:
Population Geography
Population geography is the study of the distribution and movement of human populations. Population geographers are interested in understanding why people live where they do and how population patterns change over time.
Cultural Geography
Cultural geography is the study of the different cultures of the world. Cultural geographers are interested in understanding how culture influences the way people live their lives.
Economic Geography
Economic geography is the study of the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Economic geographers are interested in understanding how economic activities are organized and how they affect the environment.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Geographic information systems (GIS) are computer systems that are used to store, analyze, and display geographic data. GIS can be used to create maps, charts, and other visualizations that can help us to understand the world around us.
Applications of GIS
GIS is used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Land use planning
- Natural resource management
- Transportation planning
- Public health
- Marketing
FAQ Compilation
What is the importance of scale and distance in geography?
Scale and distance are crucial in geography as they allow us to accurately represent and measure the spatial relationships between geographic features. They help us understand the relative sizes, distances, and proportions of different places on Earth.
How does physical geography impact human activities and the environment?
Physical geography exerts a profound influence on human activities and the environment. It shapes the availability of resources, influences transportation and communication networks, and affects agricultural practices. Understanding physical geography is essential for sustainable land use planning and environmental conservation.
What are the key factors that influence population growth and decline?
Population growth and decline are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including birth rates, death rates, migration patterns, economic conditions, and government policies. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective population management and planning.